Optimization Method Of Crankshaft Dynamic Balance
Article Source: Jp Balancing Machines
Time:2017-09-13
The dynamic imbalance of the rotating machinery is the main factor causing the mechanical vibration. Reduction and elimination of moving parts’ moving imbalance is essential to reduce the mechanical vibration of the process. As a major component of the internal combustion engine crankshaft, its balance accuracy of the machine and supporting performance is very big influence due to long axial distance, high speed. Different internal combustion engines, the crankshaft structure is different. Common are four-cylinder and six-cylinder type, and for small-scale internal combustion engine on the three-cylinder crankshaft. Recent, the crankshaft balance correction is different according to the different crankshaft type.
It is usually that balancing the crankshaft is to disperse the mass on the fixed position of the uneven resection of the crankshaft to remove to achieve the purpose of balance crankshaft. This method can achieve the balance, but not as small as possible to remove the weight. Optimization is about to minimize the removal weight to achieve the purpose of balancing crankshaft. The so-called optimization method, substantially, is to change the current 0~9O or O~12O~240 fixed position weight removal. According to the specific circumstances of each crankshaft, looking for the most appropriate point and the smallest mass is the optimizing method. For the crankshaft that cannot be fully balanced, it is possible to achieve the purpose of correcting the crankshaft as long as the majority of the unbalance is removed and the remaining unbalance is within the allowable range.
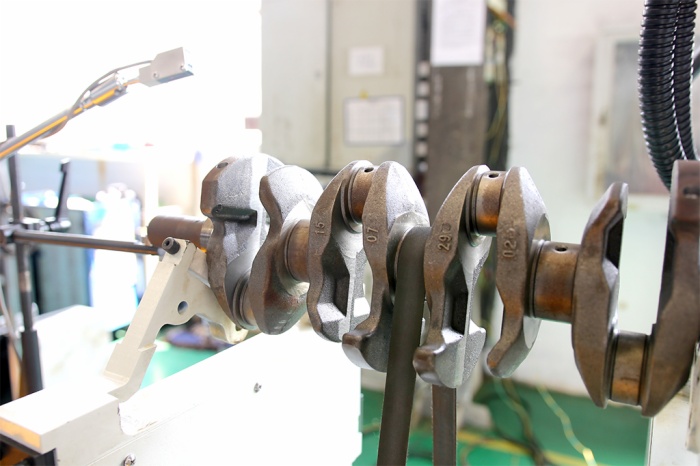

When using the optimization method, it is important to note that it is not always necessary to find the total minimum weight direction. There is a possibility that the minimum weight has the most mass on this position while the other position mass is very small. Therefore the crankshaft balance optimization method is important both in the crankshaft design process and in the crankshaft production and calibration process.



.png)
.png)

.png)
