Causes of crankshaft unbalance:
The connecting rod is mounted on the connecting rod journal of the crankshaft, and the center of connecting rod journal and the main journal have certain distance. Due to the above two journals are not concentric, when the crankshaft rotates, the inertial masses of the piston and the connecting rod cause the crankshaft losing its balance, and then generating a large unbalanced force (i.e., centrifugal force). This unbalanced force will increase the load on the main journal.
In order to eliminate this unbalanced force, the balance block need to be installed on the crankshaft to reach balance. The mass, size, shape and installation position of the balance block should be designed reasonably to overcome the centrifugal force generated in the crankshaft rotation and reduce the load on main journal.
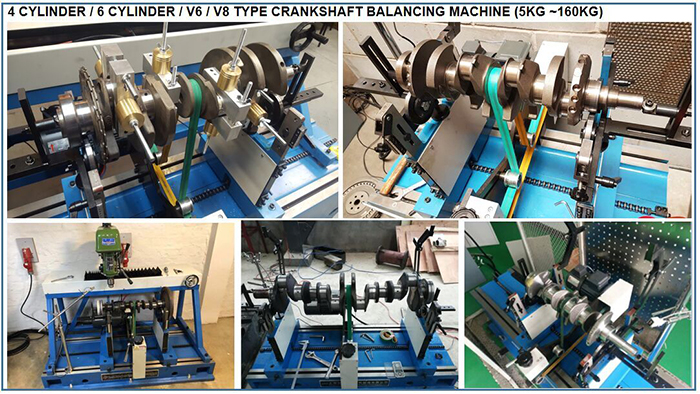
In order to eliminate this unbalanced force, the balance block need to be installed on the crankshaft to reach balance. The mass, size, shape and installation position of the balance block should be designed reasonably to overcome the centrifugal force generated in the crankshaft rotation and reduce the load on main journal.
The crankshaft dynamic balancing machine corrects the unbalance amount of the crankshaft based on the measured data, and can improve the mass distribution of the rotor with respect to the axis, so that the vibration generated when the crankshaft rotates or the vibration force acting on the bearing is reduced to an allowable range. Therefore, the balancing machine is an indispensable device for reducing vibration, improving performance and upgrading quality.


.png)
.png)

.png)
